How To Run a React Application on a Digital Ocean Droplet
Complete guide to hosting a Node API on Digital Ocean using PM2, Nginx reverse proxy & SSL
The Brief
I was creating a multiplayer, browser based minefield-esque game, where users take turns guessing where a programmatically placed dot has rendered on a canvas. With this project, I wanted to try something different. Instead of using a framework to do my bidding, I wanted to rent a server that I could host my back and frontend on.
This is the technology stack I went with:
// The core stack.- Web: TypeScript, Vite, React.- Nginx for handling SSL, reverse proxying, and load balancing (VPS only).Implementation
I already had a Digital Ocean Droplet set up. It was where I was running my backend.
1. Clone Github Repository Onto Droplet
In order to do this, I needed to generate an SSH key and add the public key to my Github repository. I followed the steps outlined in Step 4 :- Clone your private repository from GitHub to Server. I named the public key where-the-dot-client-deploy-key because I needed to distinguish between it and another SSH key that I was using to access my server Git repository.
When using multiple repositories on a single server, it is required that you use different SSH keys to access each one of your repositories. This sensible requirement is explained in Using multiple repositories on one server, screenshot below.
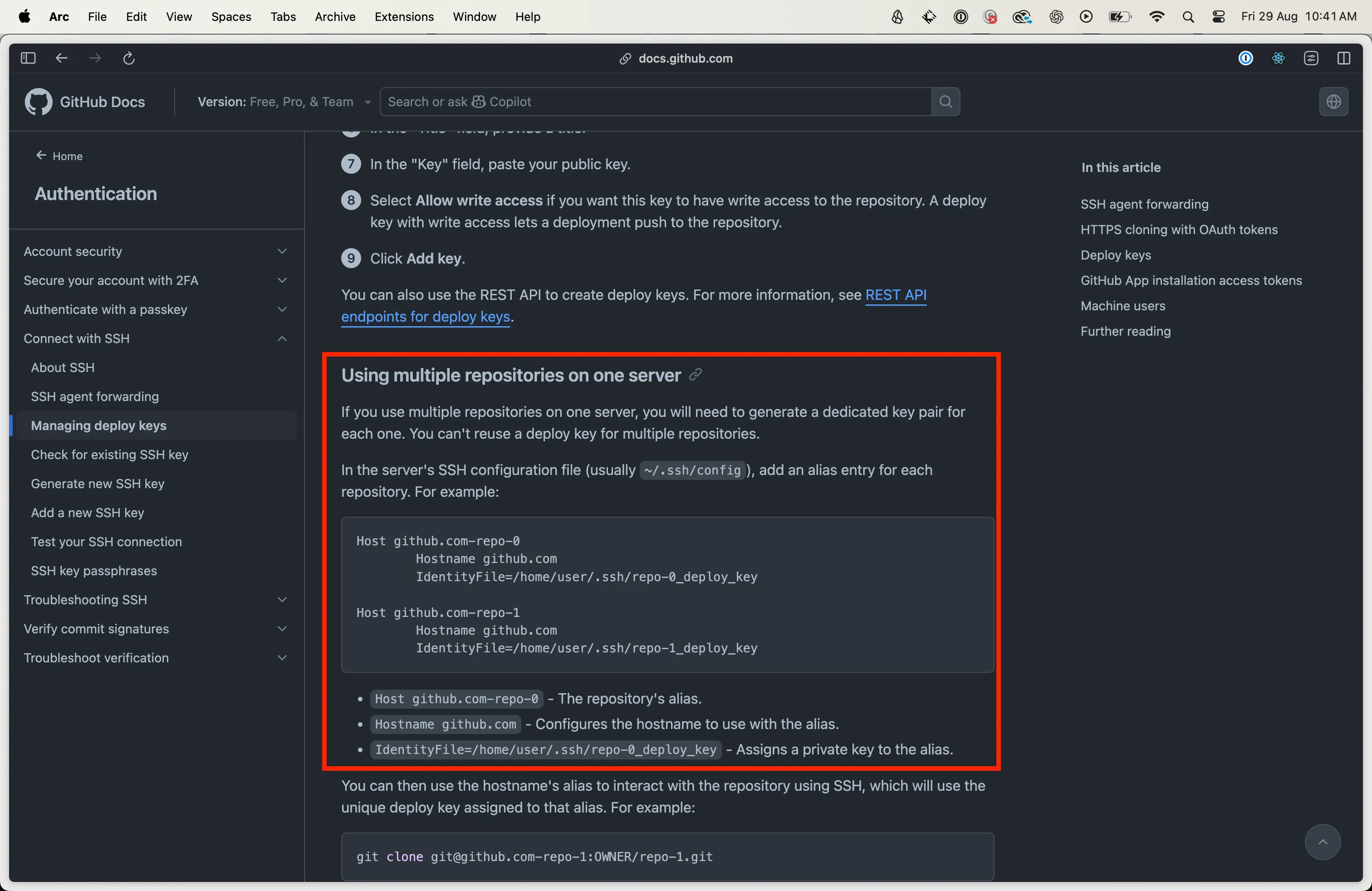
This was the entry in my ssh.config for my client repository:
Host github.com-where-the-dot-client Hostname github.com AddKeysToAgent yes IdentityFile ~/.ssh/where-the-dot-client-deploy-keyThis was my ssh.config in full:
Host github.com-where-the-dot-client Hostname github.com AddKeysToAgent yes IdentityFile ~/.ssh/where-the-dot-client-deploy-key
Host github.com-where-the-dot-server Hostname github.com AddKeysToAgent yes IdentityFile ~/.ssh/where-the-dot-server-deploy-key2. Setting Nginx as a Reverse Proxy
For my domain wherethedot.com, I needed Nginx to serve my client application. This required adding a server block to my Nginx configuration and copying my applications’ build files to Nginxs’ web directory.
I found a helpful resource in How To Deploy a React Application with Nginx on Ubuntu.
# HTTP to HTTPS redirect for main domainserver { listen 80; server_name wherethedot.com www.wherethedot.com; return 301 https://$host$request_uri;}
# Main domain - React clientserver { listen 443 ssl;
root /var/www/wherethedot.com/html; index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html;
server_name wherethedot.com www.wherethedot.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/certs/cloudflare_origin_cert.pem; ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/private/cloudflare_origin_key.pem;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3; ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# Static files (CSS, JS, images, etc.) location ~* \.(js|css|png|jpg|jpeg|gif|ico|svg|woff|woff2|ttf|eot)$ { expires 1y; add_header Cache-Control "public, immutable"; try_files $uri =404; }
# React Router - serve index.html for all other routes location / { try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html; }}After each client rebuild, I needed to copy the build files to Nginxs’ web directory. Deploy React & Node.js with HTTPS on Digital Ocean and Netlify - Part 19 was a helpful resource during this part of the process.
// Run command inside client directory (cd ~/where-the-dot-client)cp -r ./dist/* /var/www/wherethedot.com/htmlIt is important to validate and restart Nginx each time you make an edit to its configuration.
sudo nginx -tsudo systemctl reload nginxOther Considerations
I realised that I did not need to host my client code on the Droplet. All I needed was the build output. I could use SFTP to upload builds to the Droplet directly.
Alternatively, instead of serving static build files, I could configure Nginx as a reverse proxy to forward requests to a locally running instance of my React application (served from a local development server). This is the approach explained in Deploy React & Node.js with HTTPS on Digital Ocean and Netlify - Part 19.
References
- How To Deploy a React Application with Nginx on Ubuntu Helped me to understand how to configure Nginx to serve my build.
- Deploy React to DigitalOcean App Platform Is a great resource. It helped me orient myself.
- Deploy React & Node.js with HTTPS on Digital Ocean and Netlify - Part 19 Was perhaps the most useful resource. It helped me understand how to serve my client application with Nginx.